Growing Blueberries: A Guide to Cultivating Delicious Berries

Blueberries are a delightful and nutritious fruit that can be enjoyed fresh, baked into pies, or added to various recipes. If you’re interested in growing your own blueberries, this guide will provide you with simple steps to successfully cultivate these delicious berries and enjoy a bountiful harvest.
How to Grow Blueberries
Selecting the Right Blueberry Variety

Blueberries come in different varieties, each with its unique flavour, growth habit, and chilling requirements. Choose varieties that are well-suited to your climate and growing conditions. Some popular blueberry varieties include highbush blueberries (Vaccinium corymbosum) and lowbush blueberries (Vaccinium angustifolium). Consider factors like chill hours, acidity preferences, and desired harvest time when selecting the right variety.
Choosing the Planting Location

Blueberries thrive in acidic soil with a pH level between 4.5 and 5.5. Choose a sunny location in your garden that receives at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Ensure the soil is well-draining, rich in organic matter, and has good moisture retention. If your soil is alkaline, consider growing blueberries in containers or raised beds filled with acidic soil mix.
Planting Blueberries
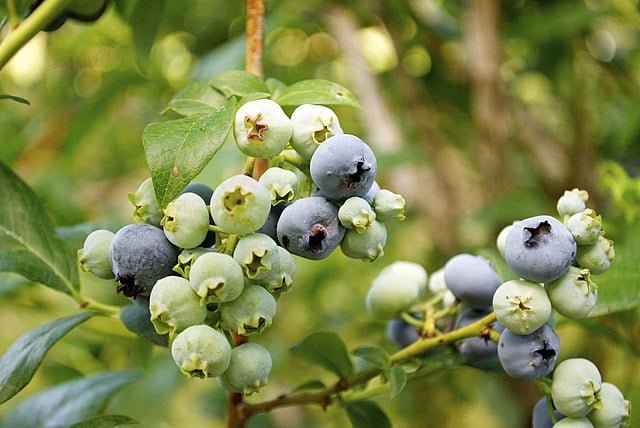

Plant blueberries in the early spring or fall when the soil is workable. Dig a hole slightly larger than the root ball of the blueberry plant. Place the plant in the hole, ensuring the top of the root ball is level with the soil surface. Back fill the hole with a mixture of peat moss, acidic compost, and soil, gently firming it around the plant. Space multiple plants about 4-6 feet apart to allow for adequate airflow and growth.
Watering and Care
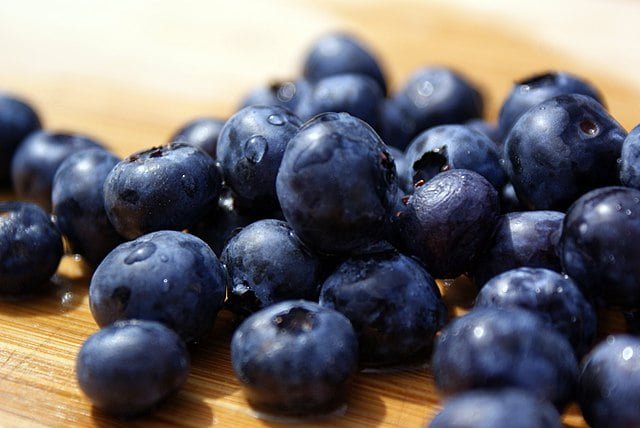

Blueberries have shallow roots and require consistent moisture. Water the plants deeply but avoid water logging the soil. Aim to keep the soil consistently moist, especially during the growing season and fruit development. Applying a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or pine needles, around the plants helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and maintain soil acidity.
Pruning and Maintenance
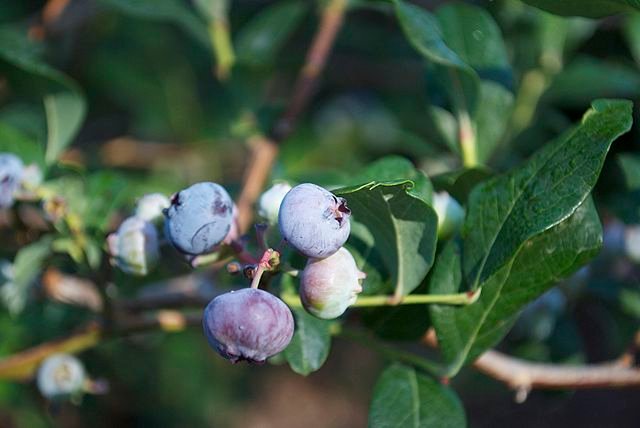

Regular pruning helps shape blueberry plants and promotes healthy growth. Prune during the dormant season to remove dead or damaged wood, thin out crowded branches, and encourage airflow. Remove any low-growing shoots or suckers that emerge from the base of the plant. Additionally, fertilize blueberries with a balanced acidic fertilizer in early spring and monitor for pests or diseases, taking appropriate measures to prevent or address any issues.
Harvesting and Enjoying
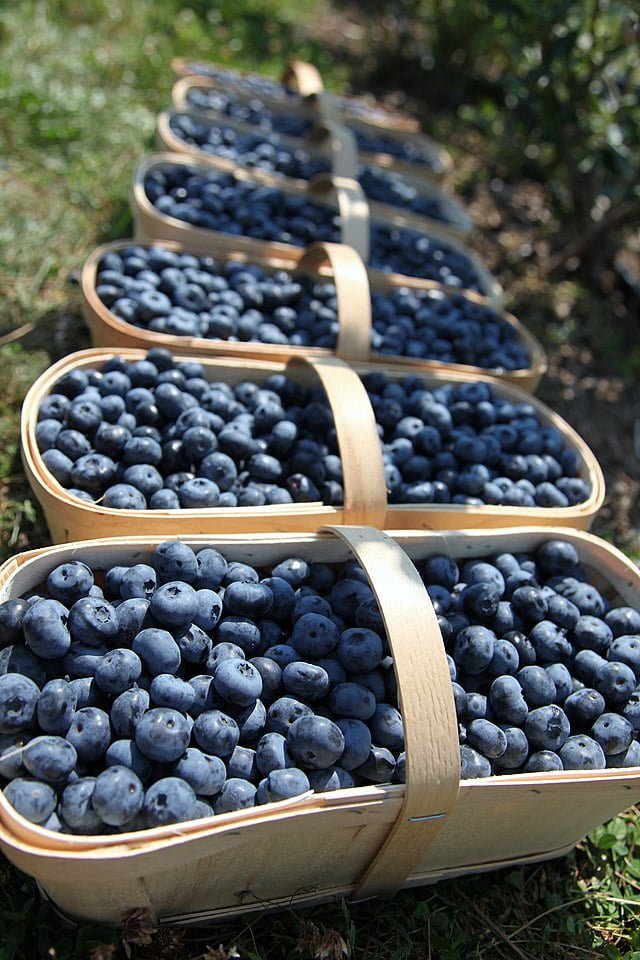

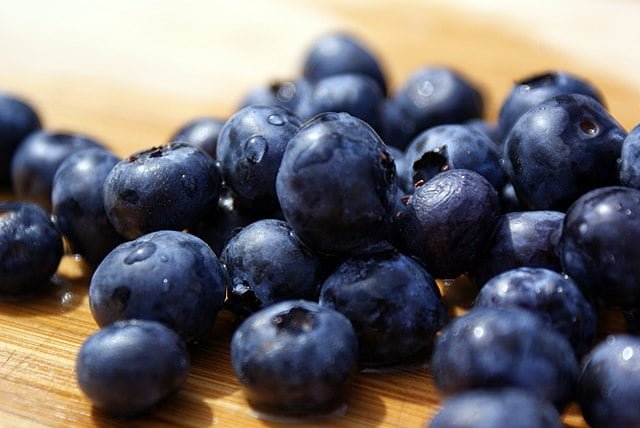
Blueberries are typically ready for harvest when they have turned a deep blue colour, usually in the summer months. Gently pick the ripe berries by hand, avoiding any green or unripe fruits. Blueberries can be enjoyed fresh, used in recipes, or frozen for later use. They are rich in antioxidants and can be a healthy addition to your diet.
Blueberries FAQ
What types of blueberry plants are there?
There are mainly three types of blueberry plants: highbush (most common in home gardens), lowbush (also known as wild blueberries), and rabbiteye (best suited for warmer climates). Each type has its own growth habits and care requirements.
How much sun do blueberry plants need?
Blueberry plants typically require full sun, which means they need at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight per day.
What soil conditions are ideal for blueberries?
Blueberries thrive in acidic soil with a pH between 4.5 and 5.5. They prefer well-draining soil rich in organic matter. If your soil isn’t naturally acidic, you may need to amend it with sulfur or use an acid-forming fertilizer.
How often should I water my blueberry plants?
Water blueberry plants regularly to keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. During dry periods, they may need more frequent watering, especially young plants and those grown in containers.
When is the best time to plant blueberries?
The best time to plant blueberries is in the early spring or late fall. This timing gives the plants a chance to establish roots in cooler temperatures before the extremes of summer heat or winter cold.
Do I need more than one blueberry plant to produce fruit?
While some blueberry varieties are self-pollinating, planting two or more varieties can significantly increase yield through cross-pollination.
How do I prune blueberry bushes?
Prune blueberry bushes in late winter or early spring before new growth begins. Remove dead or weak branches, thin out crowded areas, and trim off low-growing shoots to encourage upward growth and fruit production.
When can I expect my blueberry plants to start bearing fruit?
Blueberry plants typically start to bear fruit in their third or fourth year after planting. The yield will increase each year as the plant matures.
Additional Resources for Growing Blueberries
1. “Growing Blueberries in the Home Garden” by the Cooperative Extension: This guide covers all aspects of home blueberry cultivation, from soil preparation to pruning and harvesting.
2. “The Backyard Berry Book” by Stella Otto: A comprehensive resource on growing all types of berry plants, including detailed chapters on blueberry care, varieties, and pest management.
3. The National Gardening Association: Offers a plethora of articles, how-tos, and a community forum where you can ask questions and share tips with other gardeners about growing blueberries and more.
National Gardening Association
By following these simple steps and providing the right growing conditions, you can enjoy a fruitful blueberry harvest in your own backyard. Get ready to savour the sweet, juicy flavours of homegrown blueberries and explore the endless culinary possibilities they offer.